- What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other? Information systems (IS) store and process data and IS key concepts include, Information architecture identifies where and how information is stored, maintained and secured. Information infrastructure includes the hardware, software and telecommunications equipment, it supports organisations goals. They relate to each other by being part of the same plan. They differ as Information architecture is the plan in place within a business and the information infrastructure is the actual implementation of the plan.
- Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture. It must have the three primary areas of information which are - back up and recovery, disaster recovery and information security.
- List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture. The five requirements characteristics are, Flexibility for example being a flexible multi language business, Scalability must have room to grow, Reliability always available to customers, Availability ensures the system runs correctly and Performance of quick reliable system.
- Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture, SOA is a business driven IT architectural approach. The value of having this system in place is it supports business innovative by adapting to changes within a business. While increasing business flexibility of processes and reusing existing IT investments. The key concepts are SOA allows businesses to run current business processes and lowers downtime in creating another process, it allows businesses to plug into new services or upgrade existing ones. It allows Interoperability where computers can share information and loose coupling where services can be joined together on demand to create composite services. (XML)
- What is an event? Where the internet sends data from one system to another through a "Event" which is a business procedure of an electrical message sending information. It detects threats and opportunitites through monitoring business process. For example when someones credit card exceeds the credit limit.
- What is a service? Runs when an event happens it is the software products and appeal to a large audience. It is a valuable business process that business people can use over multiple products and businesses.
- What emerging technologies can companies can use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
Monday, August 30, 2010
Weekly Questions: Week Six - Enterprise Architectures
Chapter five questions
Monday, August 23, 2010
Weekly Questions: Week Five - Ethics and Security
Chapter Four Questions
Ethics and Security
Explain the ethical issues surrounding information technology.
There are a number of ethical issues surrounding IT. The main issues include:
-Privacy: Having your own personal space, having secure data/information and not being observed without consent.
-Confidentiality: Private messages etc are only view for the authorised or intended participants.
Others include:
- Intellectual property: Keeping knowledge & information limited.
-Copyright: Where copyrighted goods are copied illegally.
-Fair use doctrine: Unauthorized use of copyrighted goods, images and creations.
-Pirated software: Where goods are duplicated and distributed without authorization.
-Counterfeit software: A type of software piracy that occurs when fake copies of software are produced in such a way that they appear to be authentic.
http://www.ust.hk/itsc/antivirus/general/prevent.html
Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal.
If a friend is broke or poor and would like a computer program such as Microsoft Office and you burn and creat a copy of the program for free for him.
Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employee
Acceptable use property: This would be used within a company to ensure the following:
1.Will not violate any laws
2.Will not break the security
3.Will not post commercial messages
4.Will not send spam
5.Will not send mail bombs
This will ensure a employee knows what is expected from them and has guidelines on how to work ethically within the workplace.
What are the 5 main technology security risks?
The 5 main Technology security risks are as follows;
1. Human Error: Not Malicious Error created by humans. Due to lack of training or carelessness leaving computers logged on.
2. Natural Disasters: Floods, Earthquakes, Terrorist Attacks.
3.Technical Failures: Software Bugs, Hardware Crashes
4. Deliberate Acts: Sabotage, White Collar Crime
5.Management Failure: Lack of Procedure, Documentation and Training.
Outline one way to reduce each risk.
1. Human Error: Firewalls or strong passwords
2. Natural Disasters: Regularly testing backing up goods.
3.Technical Failures:Having up to date technology
4. Deliberate Acts: Develop a security plan and purchase a security package to protect against viruses
5.Management Failure: Train staff.
What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employee?
A disaster recovery plan is the process of recovering data after an organisation has been affected by a disaster. Strategies include Alternative Site to store information and back up data.
Ethics and Security
Explain the ethical issues surrounding information technology.
There are a number of ethical issues surrounding IT. The main issues include:
-Privacy: Having your own personal space, having secure data/information and not being observed without consent.
-Confidentiality: Private messages etc are only view for the authorised or intended participants.
Others include:
- Intellectual property: Keeping knowledge & information limited.
-Copyright: Where copyrighted goods are copied illegally.
-Fair use doctrine: Unauthorized use of copyrighted goods, images and creations.
-Pirated software: Where goods are duplicated and distributed without authorization.
-Counterfeit software: A type of software piracy that occurs when fake copies of software are produced in such a way that they appear to be authentic.
http://www.ust.hk/itsc/antivirus/general/prevent.html
Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal.
If a friend is broke or poor and would like a computer program such as Microsoft Office and you burn and creat a copy of the program for free for him.
Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employee
Acceptable use property: This would be used within a company to ensure the following:
1.Will not violate any laws
2.Will not break the security
3.Will not post commercial messages
4.Will not send spam
5.Will not send mail bombs
This will ensure a employee knows what is expected from them and has guidelines on how to work ethically within the workplace.
What are the 5 main technology security risks?
The 5 main Technology security risks are as follows;
1. Human Error: Not Malicious Error created by humans. Due to lack of training or carelessness leaving computers logged on.
2. Natural Disasters: Floods, Earthquakes, Terrorist Attacks.
3.Technical Failures: Software Bugs, Hardware Crashes
4. Deliberate Acts: Sabotage, White Collar Crime
5.Management Failure: Lack of Procedure, Documentation and Training.
Outline one way to reduce each risk.
1. Human Error: Firewalls or strong passwords
2. Natural Disasters: Regularly testing backing up goods.
3.Technical Failures:Having up to date technology
4. Deliberate Acts: Develop a security plan and purchase a security package to protect against viruses
5.Management Failure: Train staff.
What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employee?
A disaster recovery plan is the process of recovering data after an organisation has been affected by a disaster. Strategies include Alternative Site to store information and back up data.
Monday, August 16, 2010
Weekly Questions: Week Four Questions: eBusiness
Chapter Three Questions
1. What is an IP Address? What is it’s main function?
IP and TCP is a unique address that lays out the rules to enable data to move around the internet - its main function is for data to travel through as basic communication.
I.P means Internet Protocol - Data transferred. Every computers IP address is unique and used across networks. Webb Add + I.P.
I.P means Internet Protocol - Data transferred. Every computers IP address is unique and used across networks. Webb Add + I.P.
2. What is Web 2.0, how does it differ from 1.0?
Web 2.0 referred to as the "Live Web" It is used to collaborate and build user content and enables businesses to seek new opportunities and upgrades. Web2.0 is used on social networks to collaborate, edit and create. This is done through Tag's creating metadata, Blogs, RSS receiving feeds from websites as requested, and Wiki where information posted to maintain/manage/share knowledge. Web1.0 was a simple method used to link text over the internet now the web is linking people too. Web1.0 is one way internet and has no user participation - "One way push of info"
3. What is Web 3.0?
Is a term used to describe the evolution of Web usage and interaction among separate paths - using metadata to build intel. It encompasses the following: Transforming the web into a database, An evolutionary path to artificial intelligence, Search for information using different medias and Evolution toward 3D. Web3.0 used to search relative data and lead to A.I on the web. It is the use of a lot of data through I.P addresses.
4. What is eBusiness, how does it differ from eCommerce?
E-Business is derived from E-Commerce and is the conducting of business on the internet and the running the business as a whole - including serving customers and collaborating with business partners - E-Commerce is basically the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. E-Business is much more in depth it refers to online exchanges of information e.g online banking customers can view their accounts.
5. What is pure and partial eCommerce
Pure E-Commerce is the exchange of digital services with no physical goods. Partial E-Commerce is the physical aspects for example online shopping sites including distribution, packaging and support. On Porters Value Chain as E-Commerce increase so does Business.
6. List and describe the various eBusiness models?
eBusiness transactions take place between Buinesses and Consumers - these activities happen between two types of business relationships 1) Exchange of Products & Services between businesses B2B and 2) Exchange of Products & Services with consumers B2C.
B2B; Is the most common model and applies to businesses buying and selling to eachother over the internet through online access to data e.g ETA etc this enables businesses to have a central market from multiple buyers and sellers and create new sales channels - Their main goal is to increase market efficiency between buyers and sellers - mostly using extranets (individual companies intranets connected together) with VPN.
B2C;
The main difference between the B2B and B2C is the customers. B2B= customers/businesses and B2C= markets to consumers. B2B relations are more complex and is the dominate business force with 80% of online businesses.
http://www.prudens.com/patens/ebusiness/busmodel.html
http://www.prudens.com/patens/ebusiness/busmodel.html
7. List and describe the major B2B models?
1) Established Buyer-Supplier Relationship
This is a pre-determined one-to-one relationship between a buyer and supplier that is supported by electronic commerce technologies. Due to the aforementioned limitations associated with EDI, companies have now turned their attention towards the Internet to support these types of buyer-supplier relationships.
2) Supplier-Oriented Marketplace
In this model, both organizations and consumers use the supplier-provided marketplace. This is the most common type of B2B model. In this model, both business buyers and individual consumers use the same supplier-provided marketplace.
3) Buyer-Oriented Marketplace
Under this model, a buyer opens an electronic market on its own server and invites potential suppliers to bid on the announced Requests for Quotation (RFQs).
4) Business-to-Business Intermediary
This model is sometimes referred to as a ‘hub’ or ‘exchange’. It is established by an electronic intermediary that runs a marketplace where suppliers and buyers have a central point to come together. These B2B hubs tend to focus mainly on non-core items that may range from stationery and computers to catering services and travel. There are two types of hubs:
• Vertical - focus on an industry and provide content that is specific to the industry’s value system of buyers and suppliers.
• Horizontal - provide the same function for a variety of industries.
http://e-articles.info/e/a/title/Models-of-B2B-Commerce/
Electronic marketplaces and e-marketplaces.
1) Established Buyer-Supplier Relationship
This is a pre-determined one-to-one relationship between a buyer and supplier that is supported by electronic commerce technologies. Due to the aforementioned limitations associated with EDI, companies have now turned their attention towards the Internet to support these types of buyer-supplier relationships.
2) Supplier-Oriented Marketplace
In this model, both organizations and consumers use the supplier-provided marketplace. This is the most common type of B2B model. In this model, both business buyers and individual consumers use the same supplier-provided marketplace.
3) Buyer-Oriented Marketplace
Under this model, a buyer opens an electronic market on its own server and invites potential suppliers to bid on the announced Requests for Quotation (RFQs).
4) Business-to-Business Intermediary
This model is sometimes referred to as a ‘hub’ or ‘exchange’. It is established by an electronic intermediary that runs a marketplace where suppliers and buyers have a central point to come together. These B2B hubs tend to focus mainly on non-core items that may range from stationery and computers to catering services and travel. There are two types of hubs:
• Vertical - focus on an industry and provide content that is specific to the industry’s value system of buyers and suppliers.
• Horizontal - provide the same function for a variety of industries.
http://e-articles.info/e/a/title/Models-of-B2B-Commerce/
Electronic marketplaces and e-marketplaces.
8. Outline 2 opportunities and 2 challenges faced by companies doing business online?
Opportunities:
1) 24 hour service.
2)No retail sellers (cut out the middle man)
Challenges:
1)Negative feedback/review from minority of consumers - lead to bad reputation.
2) Correctly trained staff.Tuesday, August 10, 2010
Weekly Questions: Week Three Strategic Decision Making.
Chapter Two Questions
1. Define TPS & DSS, and explain how an organisation can use these systems to make decisions and gain competitive advantages
TPS: Transaction Processing Systems used by analysts comprises of Transactional Information: This process is used to support the performance of daily operational tasks e.g ATM's This information is used to analyze sales and demand - while determining how much inventory to carry. Also Analytical Information: used to support the performance of managerial analysis tasks - Transactional, market and industry information e.g trends, sales and product statistics, and future growth - Managers use this information before making decisions within the organisation. Other TPS are Online transaction processing OLTP and Transaction processing sys TPS and Online analytical processing OLAP.
DSS: Decision Support Systems used by Managers mainly and like the TPS system these ensure that businesses have information available and to assist in decision making processes and problems solving and opportunity solving. EIS: Executive Information Systems used by Executives to analyse data internally and externally within an organisation - consolidation of information, Drill down information within a desired time period and Slice and dice information from different perspectives.
TPS: Transaction Processing Systems used by analysts comprises of Transactional Information: This process is used to support the performance of daily operational tasks e.g ATM's This information is used to analyze sales and demand - while determining how much inventory to carry. Also Analytical Information: used to support the performance of managerial analysis tasks - Transactional, market and industry information e.g trends, sales and product statistics, and future growth - Managers use this information before making decisions within the organisation. Other TPS are Online transaction processing OLTP and Transaction processing sys TPS and Online analytical processing OLAP.
DSS: Decision Support Systems used by Managers mainly and like the TPS system these ensure that businesses have information available and to assist in decision making processes and problems solving and opportunity solving. EIS: Executive Information Systems used by Executives to analyse data internally and externally within an organisation - consolidation of information, Drill down information within a desired time period and Slice and dice information from different perspectives.
2. Describe the three quantitative models typically used by decision support systems.
1. Sensitivity analysis: Studies the impact of changes and how these changes affect other variables.
2. What-if analysis: Studies the impact of change in an assumption and analysts continue to repeat this in various situations
3. Goal seeking analysis: Studies the inputs used to achieve a desired goal by setting target value/goals for a variable and then changes other variables until the target/goals is a achieved.
1. Sensitivity analysis: Studies the impact of changes and how these changes affect other variables.
2. What-if analysis: Studies the impact of change in an assumption and analysts continue to repeat this in various situations
3. Goal seeking analysis: Studies the inputs used to achieve a desired goal by setting target value/goals for a variable and then changes other variables until the target/goals is a achieved.
3. Describe a business processes and their importance to an organisation.
"A business process is a standardised set of activities that accomplish a specific task, such as processing a customers order". E.g Paying for groceries "Purpose" at the checkout "Process. These processes transform a set of inputs into a set of outputs (goods or services) while ensuring organisations "anticipate bottlenecks, eliminate duplicate activities, combine related activities and identify smooth running processes - while achieving goals.
"A business process is a standardised set of activities that accomplish a specific task, such as processing a customers order". E.g Paying for groceries "Purpose" at the checkout "Process. These processes transform a set of inputs into a set of outputs (goods or services) while ensuring organisations "anticipate bottlenecks, eliminate duplicate activities, combine related activities and identify smooth running processes - while achieving goals.
4. Compare business process improvement and business process re-engineering.
"Business Process Improvement attempts to understand and measure current process and make performance improvements accordingly".
Business Process Re-engineering "assumes that the current process is irrelevant, does not work, or is broken and must be overhauled from scratch". Looks at taking a completely different path instead of trying to improve the current process.
"Business Process Improvement attempts to understand and measure current process and make performance improvements accordingly".
Business Process Re-engineering "assumes that the current process is irrelevant, does not work, or is broken and must be overhauled from scratch". Looks at taking a completely different path instead of trying to improve the current process.
5. Describe the importance of business process modelling (or mapping) and business process models.
Business Process Modelling is created to ensure businesses have a detailed flowchart or process map of desired goals and the tasks/inputs and activities needed.
Business Process Models expose process detail and in a controlled manner, encourage conciseness and accuracy in describing the process model, focus attention on the process model interfaces and provide a powerful process analysis and consistent design vocabulary. E.g As -is process to To-be process of ordering a hamburger.
http://www.business-persuasion-influence-motivation.com/process-mapping.html
Weekly Questions: Week Two Information Systems in Business.
Chapter One Questions
Explain information technology’s role in business and describe how you measure success?
IT role is being an enabler of Business success and Innovation. IT automates business processes and communication.
It can transform a business, reduce costs, improve productivity and generate growth.
http://www.quickmba.com/strategy/generic.shtml
List and describe each of the forces in Porter’s Five Forces Model?
Determines the relative attractiveness of an industry:
BSTTR
Buyer Power:HIGH Ecommerce more choice -LOW =LOYALTY PROGRAM
Supplier Power: LOW Reduced bigger market, power, LOW when choice is many(suppliers want LOW, Org HIGH)
Threat of SUBSTITUTE P&S: Increases rivalry, alternatives, options = switching costs.
Threat of NEW entrants:HIGH Marketing new P&S High within IT, Online, LOW when barriers Telstra
Rivalry among existing competitors HIGH when market is fierce LOW when competition is complacent.= “switching costs steal customers”
http://notesdesk.com/notes/strategy/porters-five-forces-model-porters-model/
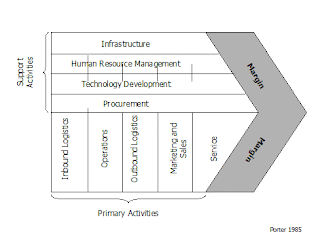
Describe the relationship between business processes and value chains?
Used to determine the success or failure of its chosen strategy:
VALUE CREATION = BUSINESS PROCESSES (standard activities that accomplish tasks) + EFFICIENT VALUE CHAINS (series of Processes -each that adds value to P&S).
Creation: Primary Value Activities PVA -Raw materials, make, market, sell and provide support. **Increase PVA decreases the threat of substitutes**
Support Value Activities SVA - Support the PVA**Increase SVA decrease new entrants**
CUSTOMERS DETERMINE EACH ACTIVITY AND HOW IT ADDS VALUE TO THE P&S
http://www.themanager.org/models/valuechain.htm
Compare Porter’s three generic strategies?
Broad cost Leadership: being a low cost producer/ selling price beats profit of rivals, competition may match but suffer losses - targets broad market, can start to produce cheaply(lower cost materials) - last a long time. Using VERTICAL INTEGRATION DECISIONS - RISKS all lower cost e.g. due to IT
Broad differentiation:P&S that has developed unique attributes n valued by customers, some firms may charge premium price due cusomter not finding substitutes RISKS: Imitations by competitiors and change in customer tates.
Focused strategy: attempts to achieve either cost advantage or differentiation - high customer loyalty and discourages competition.RISKS: Imitation and cost leaders adapt products and compete.
http://www.elearnmag.org/subpage.cfm?section=tutorials&article=17-2
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)