Chapter One Questions
Explain information technology’s role in business and describe how you measure success?
IT role is being an enabler of Business success and Innovation. IT automates business processes and communication.
It can transform a business, reduce costs, improve productivity and generate growth.
http://www.quickmba.com/strategy/generic.shtml
List and describe each of the forces in Porter’s Five Forces Model?
Determines the relative attractiveness of an industry:
BSTTR
Buyer Power:HIGH Ecommerce more choice -LOW =LOYALTY PROGRAM
Supplier Power: LOW Reduced bigger market, power, LOW when choice is many(suppliers want LOW, Org HIGH)
Threat of SUBSTITUTE P&S: Increases rivalry, alternatives, options = switching costs.
Threat of NEW entrants:HIGH Marketing new P&S High within IT, Online, LOW when barriers Telstra
Rivalry among existing competitors HIGH when market is fierce LOW when competition is complacent.= “switching costs steal customers”
http://notesdesk.com/notes/strategy/porters-five-forces-model-porters-model/
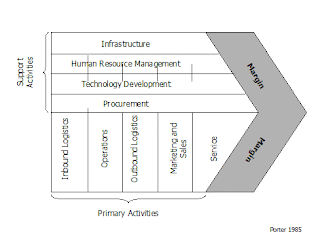
Describe the relationship between business processes and value chains?
Used to determine the success or failure of its chosen strategy:
VALUE CREATION = BUSINESS PROCESSES (standard activities that accomplish tasks) + EFFICIENT VALUE CHAINS (series of Processes -each that adds value to P&S).
Creation: Primary Value Activities PVA -Raw materials, make, market, sell and provide support. **Increase PVA decreases the threat of substitutes**
Support Value Activities SVA - Support the PVA**Increase SVA decrease new entrants**
CUSTOMERS DETERMINE EACH ACTIVITY AND HOW IT ADDS VALUE TO THE P&S
http://www.themanager.org/models/valuechain.htm
Compare Porter’s three generic strategies?
Broad cost Leadership: being a low cost producer/ selling price beats profit of rivals, competition may match but suffer losses - targets broad market, can start to produce cheaply(lower cost materials) - last a long time. Using VERTICAL INTEGRATION DECISIONS - RISKS all lower cost e.g. due to IT
Broad differentiation:P&S that has developed unique attributes n valued by customers, some firms may charge premium price due cusomter not finding substitutes RISKS: Imitations by competitiors and change in customer tates.
Focused strategy: attempts to achieve either cost advantage or differentiation - high customer loyalty and discourages competition.RISKS: Imitation and cost leaders adapt products and compete.
http://www.elearnmag.org/subpage.cfm?section=tutorials&article=17-2


Managing Info sys (MIS)= Strategic goals, information systems and meeting goals.
ReplyDeleteIMPORTANT:
1)Data: raw facts that describe the characteristic of an even - name exp etc
2)Information: Data converted into meaningful context.
3)Business Intelligence: Applications and information that are used within a business to gather and analyse data and info to support decision making process e.g demo, age etc of raod accidents
DIBI
Roles within IT
Chief Info Officer (CIO):oversees all uses of IT, strategic alignment of IT with business golas/objectives -MAnager, leader of IT vision alines with Business vision, Comm: builder relationships BETWEEN business n IT personnel
Chief Tech Officer (CTO)Maintaing It within a business e.g speed, accuracy and security of IT sys
Chief Security Officer (CSO)Ensures security of IT sys
Chief Privacy Offier (CPO)Ensuring the ethical n legal use of info
Chief Knowledge Office (CKO)collecting, maintaining n distributing organisations knowledge.
ITSPK
KPI’s: Measures that are tied to business drivers.
EFFICIENCY AND EFFECTIVENESS MATRICS:
Efficiency IT metric: Measures SUCCESS & performance of an IT system.
Focus on TECHNOLOGY- Speed, availability, info and response time.
E.G TIME to repair: How long to resolve a problem
FIRST fixed rate, Change success rate percentage
Effectiveness IT metric: Measures the IMPACT of IT on business process and activities - customer satisfaction, sales. Accomplishing goals.
Focus on organisation GOALS, strategy and objectives - user friendly, satisfaction, Financial
BENCHMARKS:Baseline values the system seeks to attain.
BENCHMARKING:process of measuring systems results, comparing and identifying improvements
IDENTIFYING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES:
Competitive Advantage: P&S greater value than of competitors.
First mover advantage: Impacting the market share by being the first market with a competitor advantage